Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are a class of therapeutics that have revolutionized the medical landscape. In recent years, mAbs have been utilized to treat a variety of diseases, ranging from autoimmune disorders to cancer.
A few numbers to get you started, just to demonstrate the importance and rapid growth rate of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. In 2018 the value of global therapeutic monoclonal antibody market was about $115.2 billion. However, in 2025 it is expected to generate $300 billion revenue.1
This article will provide an overview of mAbs and their current applications in the healthcare space.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are single-chain proteins produced in the lab through a cloning process that uses immortal cell lines, such as myeloma cells or hybridomas. These proteins are specific for one type of antigen and are used to recognize and bind to it with high affinity. The therapeutic potential of mAbs lies in their ability to selectively target diseased cells while avoiding healthy ones.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get all the latest updates, and learn about our advancements in antibody production.
Subscribe now
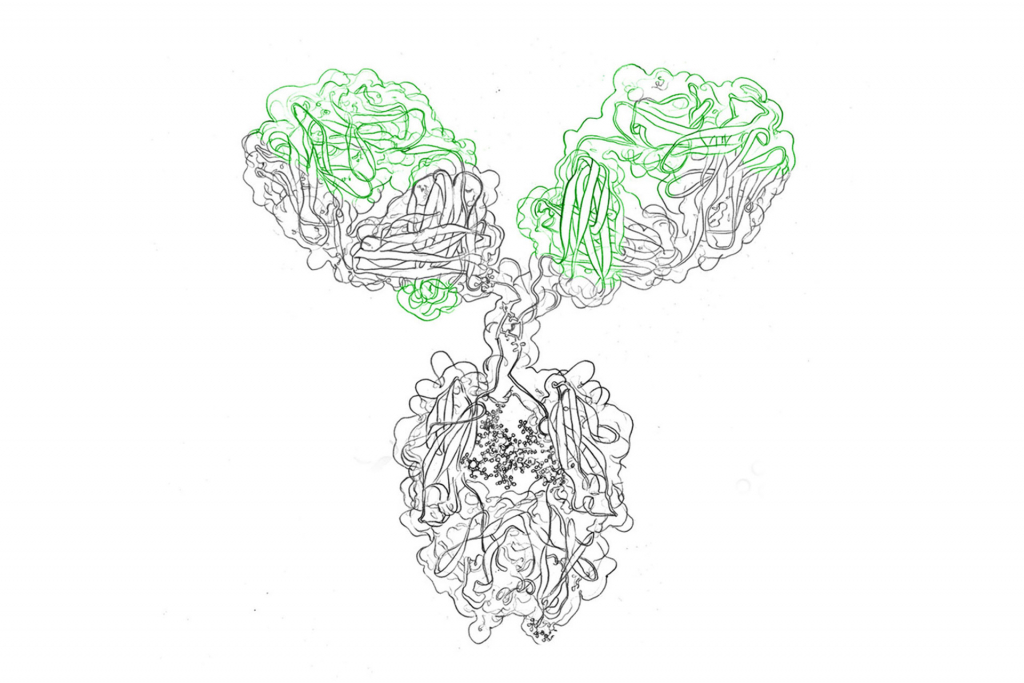
The mechanism of action for therapeutic mAbs is complex but can be broken down into two main processes: binding and signaling. First, the mAb binds to its antigen on the surface of the target cell, forming an antigen-antibody complex. The binding triggers a signal transduction cascade within the cell that can lead to either activation or inhibition depending on how it is designed. For example, some mAbs act by activating an intracellular signaling pathway leading to apoptosis—the death of cells—while others work by blocking pathways leading to cell proliferation or inflammation.
One of the primary benefits of therapeutic monoclonal antibody therapy is that it is highly specific and effective at targeting only diseased cells while leaving healthy cells unharmed. Additionally, since they are genetically engineered molecules, they can be tailored to fit the specific needs of different patients and diseases—making them more effective than traditional treatments like chemotherapy or immunosuppressants. Finally, because mAbs are so versatile, they can be used to treat a wide range of diseases—from cancer to autoimmune disorders—and can even be used as prophylactic treatments to prevent certain conditions before they occur.
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies have become an important part of modern medicine due to their specificity and effectiveness in treating various conditions. By binding directly to diseased cells while leaving healthy cells unharmed, mAbs provide targeted treatment with minimal side effects. Furthermore, because mAbs can be tailored to meet individual patient needs and are capable of treating a wide range of ailments, they offer researchers and clinicians an invaluable tool for combatting some of today’s most challenging illnesses. As research continues in this area, we look forward to seeing what new breakthroughs therapeutic monoclonal antibody therapy has in store for us!
Monoclonal antibodies – all information
What is a monoclonal antibody?
Difference between monoclonal & polyclonal & recombinant