Recombinant monoclonal antibody production
We are a leading service provider for recombinant antibody production. Get in contact!
Antibody characterization is an important step in the production of antibodies and therefore essential for various scientific fields. Nevertheless, antibodies stand as remarkable entities with immense potential across a spectrum of domains, ranging from diagnostics and research to therapeutic interventions. Their exceptional specificity and adaptability render them indispensable tools for deciphering, targeting, and addressing a wide range of biological elements.
In this article, we’ll delve into the pivotal field of antibody characterization and its profound significance in ensuring the quality and effectiveness of these molecules in diverse applications. We’ll navigate the methods, techniques, and parameters that empower researchers and developers to unlock the full potential of antibodies, highlighting the role of antibody characterization.
Antibodies play a pivotal role in healthcare, research, and drug discovery by recognizing specific molecules like pathogens and target proteins. To harness their potential fully, meticulous characterization of antibodies is essential. This process unveils their properties and guides their application.
In antibody engineering, understanding an antibody’s behavior is crucial. Whether derived from hybridoma technology or phage display, thorough antibody characterization ensures their specificity, binding affinity, and stability. This knowledge drives drug discovery, helping identify candidates with therapeutic potential. Additionally, characterizing antibodies streamlines production workflows, optimizing conditions and reducing resource expenditure.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get all the latest updates, and learn about our advancements in antibody production.
Subscribe now
Antibody characterization involves a sophisticated array of advanced methods and techniques, strategically designed to unveil intricate details about these potent molecules.
Some important antibody characterization methods include:
By harnessing such approaches, researchers gain invaluable insights into properties that not only underpin their functionality but also define their potential applications.
In the following chapters, we will take a look at important types of antibody characterization methods, including some relevant examples.
Assays play an instrumental role in assessing diverse facets of antibody behavior. Employing techniques such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and fluorescence spectroscopy, researchers gain access to both quantitative and qualitative dimensions of binding interactions.
Alongside these, mass spectrometry and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) uncover multifaceted structural nuances and binding kinetics. These assays serve as a gateway, enabling the precise determination of antibody specificity and providing a roadmap for accurate epitope mapping on target antigens.
Furthermore, these techniques are pivotal in identifying potential peptide targets and gaining insights into the dynamics of antibody-antigen binding, whether it’s within the controlled environment of cell culture or the intricacies of in vivo settings.
Delving deeper into antibody characteristics necessitates the application of analytical techniques like sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and mass spectrometry.
Through SDS-PAGE, researchers not only gain insights into molecular weight, but also untangle possible post-translational modifications. On a more intricate level, mass spectrometry reveals the minutiae, encompassing amino acid sequences and intricate patterns of residues. These techniques assume a vital role in the detection of impurities and contribute to the overall integrity of antibodies.
At the core of effective antibody functionality lies a comprehensive understanding of interactions between antibodies and antigens. Techniques such as surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and bio-layer interferometry offer an unfolding narrative, revealing real-time insights into the dynamic kinetics governing these interactions.
This data not only sheds light on the strength and stability of antibody-antigen bonds but also bears immense significance in the realm of therapeutic antibodies. Furthermore, this data paves the way for precise delineation of binding specificity, a pivotal cornerstone in designing potent antibody-based interventions.
Unraveling the tapestry of antibody heterogeneity and variants forms an integral facet of maintaining consistent quality. Techniques such as mass spectrometry and high-throughput sequencing serve as illuminating lenses, highlighting variations within antibody samples.
This insightful comprehension guides optimization of cell culture processes and ensures the desired attributes of both monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and polyclonal antibodies. Notably, quantitative approaches also step in, aiding the assessment of immunoglobulin G (IgG) subclasses, thereby significantly impacting therapeutic applications and enabling accurate quantification.

The exploration of antibody characteristics encompasses a breadth of dimensions, extending beyond structural and functional insights. Delving into a multifaceted array of parameters offers a comprehensive grasp of their quality, efficacy, and potential applications.
An essential facet of antibody behavior lies in understanding the recognition of the target epitope and the intricacies of binding specificity. Techniques such as epitope mapping shed light on the molecular landscapes where these interactions unfold. These insights not only unravel the complexities of antibody-antigen binding but also empower the design of tailored interventions, whether for therapeutics or diagnostics.
The profound influence of glycosylation and post-translational modifications on antibody behavior cannot be overstated. Scrutinizing these modifications reveals insights into stability, potency, and safety. This knowledge is pivotal in shaping therapeutic potential and optimizing the overall efficacy of antibodies, be they naturally derived or recombinant.
Learn more on glycosylation of proteins
The structure and conformation of antibodies form the bedrock of their functionality and stability. Techniques like X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy unveil the intricate three-dimensional arrangements that govern their behavior. These revelations provide critical insights into their functions, modifications, and interactions at the binding site level, ensuring both biochemical accuracy and therapeutic relevance.
Detecting and mitigating impurities and aggregation within antibody samples is of paramount importance to ensure their safety and efficacy. Leveraging techniques that pinpoint these issues precisely enables researchers to optimize production processes, safeguard therapeutic potential, and uphold the integrity of vital reagents and experimental systems.
We are a leading service provider for recombinant antibody production. Get in contact!
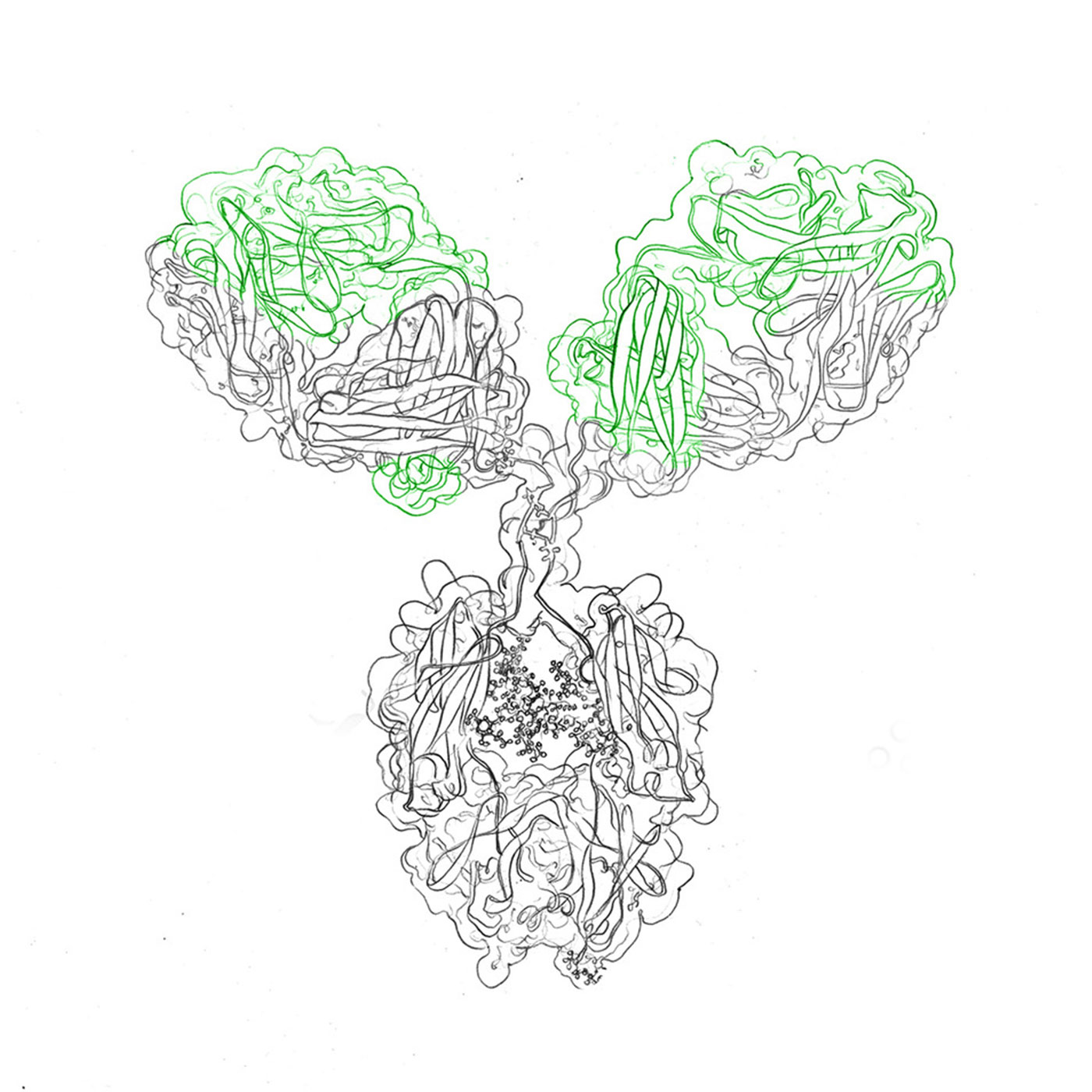
The intricate journey from antibody discovery to clinical application is navigated through a meticulous process punctuated by pivotal checkpoints, where antibody characterization emerges as an indispensable cornerstone within the expansive realm of drug development.
Employing advanced methodologies, for instance to dissect receptor interactions and behavior in vitro, forms a crucial component of antibody characterization. Understanding the mechanism of fusion proteins, interactions with cellular cell lines, and the potential immunogenicity of these constructs is imperative to develop new therapeutic modalities.
At the heart of antibody characterization lies its vital role in quality control throughout the spectrum of drug development. From inception to scaled production, thorough characterization ensures unwavering adherence to predefined specifications.
Techniques including ELISA, mass spectrometry, and SDS-PAGE dissect elements such as purity, molecular weight, and post-translational modifications. This scrutiny safeguards the inherent integrity of the final product.
Complementing this, the rigorous validation of these characterization methods establishes a bedrock of dependability, precision, and reproducibility. This validation is extremely important in satisfying stringent regulatory standards, while simultaneously underpinning patient safety, an overarching concern in the sphere of healthcare.
When dealing with therapeutic antibodies, the import of comprehensive characterization escalates remarkably. An intricate understanding of antibody attributes, including binding specificity, stability, and potential immunogenicity, becomes paramount.
Emerging from techniques like kinetics analysis, this understanding guides the strategic selection of candidates for rigorous clinical trials. The foundation of robust characterization data empowers researchers and developers to design clinical trials that yield pivotal insights, substantially augmenting the prospects of clinical success.
In the ever-evolving panorama of Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs), the significance of characterization is accentuated even further. ADCs pivot on the delicate equilibrium between the antibody and the pharmacologically active payload.
Accurate quantitation of drug-antibody ratios, meticulously confirmed through methodologies such as mass spectrometry and binding assays, constitutes the cornerstone for ensuring the intended efficacy of these potent hybrids. Through meticulous characterization, researchers evaluate the stability and bioactivity of ADCs, a pivotal facet within the realm of modern biopharmaceutical advancements.
At evitria, we have expert knowledge in all aspects of recombinant antibody production, including antibody characterization. Based on CHO cells, we offer recombinant antibody production services for different applications – from lab to large-scale.
From antibody development to advanced antibody purification and characterization methods – the process of antibody production requires high levels of expertise and resources. By taking off this complex task, we keep our customers’ backs free in their efforts to achieve new advances based on recombinant antibodies.
Antibody characterization is the process of analyzing and understanding the properties and behaviors of antibodies, including their interactions, binding affinity, stability, and modifications. It involves using various techniques to gain insights into the structure and function of these molecules, which is crucial for research, diagnostics, and therapeutic applications.
Antibody characterization is important because it provides essential insights into antibody properties, enabling effective drug development, ensuring product quality, precise diagnostics, tailored therapies, optimized workflows, and regulatory compliance.